What Are the Steps to Master CVC Sentences for ESL Learners?
Want to read simple sentences easily? Many ESL learners struggle to assemble basic sentences, which leads to frustration and slow progress.
But what if there was a proven method to help you read and write simple sentences quickly?
Introducing CVC sentences – the building blocks of the English language. You can rapidly improve your reading and writing skills by focusing on words that follow the consonant-vowel-consonant pattern.
In this blog post, we’ll share essential tips to help you master CVC sentences, boosting your confidence and fluency in English.
Get ready to improve your language skills to the next level with this powerful technique, which has helped countless ESL learners succeed!
Fundamental Components for Teaching CVC Sentences
1. Understanding Phonemes
| Phoneme | Example Words |
|---|---|
| S | sit, sun, sock |
| A | cat, map, bat |
| T | top, tin, bat |
| P | pin, tap, mop |
| I | sit, pin, lip |
| N | net, pin, sun |
Phonemes are the smallest units of sound in spoken language. They play a crucial role in teaching reading through phonics, as they help children decode words by understanding the sounds associated with each letter or group of letters.
By learning phonemes, students can break down words into smaller, more manageable parts, making them easier to read and understand.
SATPIN is a set of six phonemes (s, a, t, p, i, n) often taught first to beginners. These sounds are chosen because they are common in many simple words and can be combined to form various CVC words.
2. The Role of Graphemes, Digraphs, Trigraphs, and Blends
| Element Type | Description | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Graphemes | Single letters representing sounds | cat, dog, big |
| Digraphs | Two letters making one sound | ship, chat, thud |
| Trigraphs | Three letters making one sound | night, right |
| Blends | Two or more consonants blended, but each sound is heard | stop, blend, crust |
CVC words can incorporate various graphemes, digraphs, trigraphs, and blends. For example, “cat” is a simple CVC word using single-letter graphemes.
The word “ship” is a CVC word that includes a digraph (“sh”). The word “night” is a CVC word with a trigraph (“igh”).
Lastly, the word “stop” is a CVC word that contains a blend (“st”). Students can expand their phonetic awareness and improve their reading skills by identifying and using these elements.
Tools and Resources Required for Learning CVC Sentences

1. Interactive Tools and Games for Practice
Incorporate interactive tools and games to reinforce learning through fun activities.
Online phonics games and mobile apps offer engaging ways for students to practice CVC words and sentences.
Look for resources that provide instant feedback and adapt to individual learning paces.
2. Worksheets and Visual Aids for Classroom Use
Use effective worksheets and visual aids to enhance teaching and cater to different learning styles.
Picture-matching activities, fill-in-the-blank exercises, and color-coded word families can help students visualize and internalize CVC patterns.
Ensure worksheets are well-designed and aligned with your teaching objectives.
A Step-By-Step Process for Teaching CVC Words
1. Warm-up with Phoneme Segmentation
Before diving into CVC words, start with phoneme segmentation activities.
Use sound boxes or have students tap their arms as they say each sound in a word. This helps them isolate and identify individual sounds within CVC words, laying the foundation for decoding and blending.
2. Decoding and Blending Sounds to Form Words
Once students are comfortable with phoneme segmentation, teach them to decode individual sounds and blend them into whole words. For example, demonstrate how the sounds /c/, /a/, and /t/ blend to form the word “cat.”
Provide ample practice with various CVC words like “dog,” “hat,” and “pin.”
3. Practical Application in Forming Sentences
After students have decoded and blended CVC words, show them how to construct simple sentences using them. Start with basic structures like “The cat sat” or “A red hat.” This promotes comprehension and encourages the use of CVC words in context.
Challenges and Solutions in Teaching CVC Sentences to ESL Learners
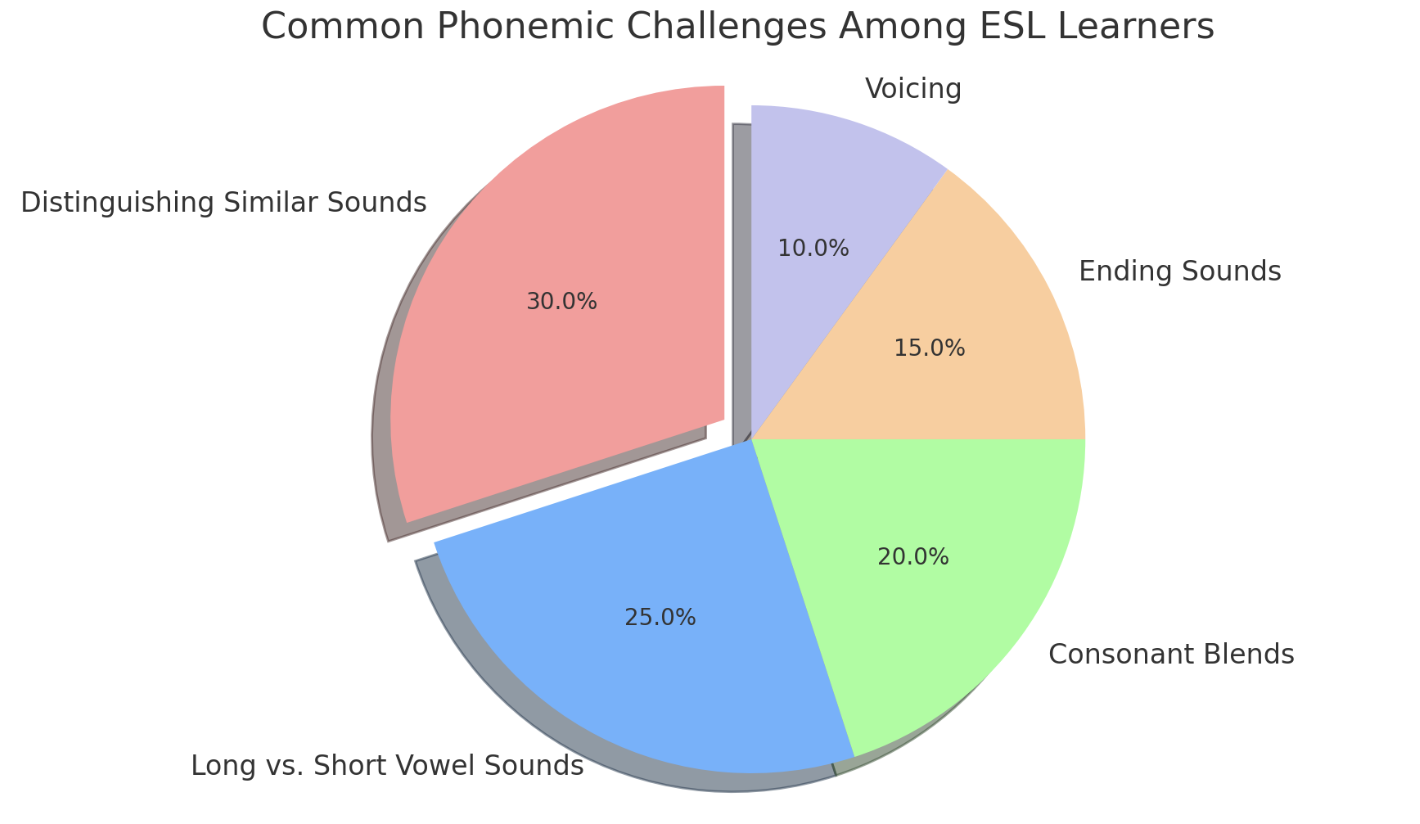
1. Common Difficulties Faced by ESL Students with CVC Sentences
ESL learners often struggle to distinguish similar sounds, such as /b/ and /p/ or /i/ and /e/.
They may also find it challenging to understand English sentence structure and word order, which can differ from their native language.
2. Tailored Approaches to Overcome These Challenges
- Emphasizing Phonological Awareness: To help ESL students overcome difficulties with similar sounds, focus on developing their phonological awareness. Use rhymes, alliteration, and sound discrimination to highlight the subtle differences between sounds. Regularly review and contrast problematic sound pairs.
- Reinforcement Through Repetition and Engaging Activities: Provide ample opportunities for repetition and practice through engaging activities. Use songs, chants, and games that target specific CVC words and sentence structures. For example, have students participate in a “CVC Word Hunt” around the classroom or play “CVC Bingo” to keep them motivated and interested.
Advanced Techniques for Mastering CVC Sentences

1. Incorporating Digraphs and Alternative Spellings in Advanced Lessons
Once students have mastered basic CVC words, introduce more complex phonetic patterns like digraphs (e.g., “sh,” “ch,” “th”) and alternative spellings (e.g., “ai,” “oa,” “ee”).
Incorporate these patterns into CVC sentences to expand their reading and writing skills.
2. Transitioning from Simple CVC Sentences to Complex Structures
Gradually introduce longer and compound words to help learners transition from simple CVC sentences to more complex structures.
For example, change “The cat sat” to “The black cat sat on the red mat.” Please encourage students to combine CVC words to create unique sentences, fostering creativity and autonomy in their language learning journey.
Conclusion
Mastering CVC sentences is a crucial step for ESL learners to build a strong foundation in English reading and writing.
Students can quickly grasp the basics of forming simple sentences by understanding phonemes, blending sounds, and practicing with engaging activities.
While challenges may arise, educators can help learners overcome difficulties through targeted strategies and progressive teaching techniques.
As you continue your English language journey, remember that CVC sentences are just the beginning. With dedication and practice, you’ll soon be able to construct more complex sentences and confidently express yourself.
So, take the next step in your learning: apply these techniques, seek out new resources, and don’t be afraid to make mistakes. Every effort brings you closer to fluency, and we’re here to support you every step of the way.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a CVC Pattern for Beginners?
CVC patterns for beginners are simple words like “cat,” “dog,” and “pen.”
How Can I Improve My CVC Fluency?
Practice segmenting, blending sounds, and reading CVC words in context to improve CVC fluency.
How Do You Decode CVC Words?
Decoding CVC words involves identifying individual sounds (phonemes) and blending them.
What Are CVC Words for Ell Students?
CVC words for ELL students are basic, three-letter words that help build foundational reading skills.
What is the CVC Rule in Phonics?
The CVC rule in phonics refers to words composed of a consonant, a vowel, and a consonant, like “cat” or “dog.” These are used to teach basic reading skills.







